Powering Up The Versatility and Reliability of Diesel Generators for Temporary Power Needs

Introduction
In a world heavily reliant on electricity, power outages can disrupt daily life and business operations. Whether due to natural disasters, maintenance work, or remote locations lacking access to the grid, temporary power solutions are essential to keep things running smoothly. Diesel generators have long been a popular choice for providing backup power in such situations, thanks to their reliability, efficiency, and ease of use. In this article, we will explore the versatility and benefits of diesel generators for temporary power needs, delving into their working principles, applications, maintenance requirements, and environmental impact.
Understanding Diesel Generators
A diesel generator is a combination of a diesel engine and an electric generator (alternator) that produces electricity through the combustion of diesel fuel. The diesel engine converts the chemical energy stored in diesel fuel into mechanical energy through combustion, which then drives the electric generator to produce electrical energy. This process is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a magnetic field is created by the movement of electrical current within a coil of wire.
Diesel generators come in various sizes and configurations to suit different power requirements, ranging from small portable units for residential use to large industrial generators capable of powering entire facilities. They are classified based on their power output, measured in kilowatts (kW) or megawatts (MW), and are designed to provide backup power during planned or unplanned outages.
Applications of Diesel Generators for Temporary Power Needs
Diesel generators find widespread application in a variety of settings where reliable backup power is essential. Some common applications include:
1. Emergency Backup Power: Diesel generators are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to provide backup power during grid outages or emergencies. They ensure that critical systems such as security systems, refrigeration units, medical equipment, and communication networks remain operational.
2. Construction Sites: Construction projects often take place in remote locations or areas without access to the grid. Diesel generators are used to power tools, lighting, and other equipment on construction sites, enabling work to continue smoothly without interruptions.
3. Events and Festivals: Outdoor events, concerts, festivals, and temporary installations require a reliable source of power to run lighting, sound systems, and other equipment. Diesel generators are often employed to provide temporary power for such events.
4. Telecommunications: Telecommunication towers and networks require uninterrupted power to ensure seamless connectivity. Diesel generators serve as backup power sources for telecommunication infrastructure, especially in remote areas or during grid failures.
5. Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals, clinics, and medical centers rely on continuous power supply to operate life-saving equipment, maintain climate control, and ensure lighting in critical areas. Diesel generators act as a reliable backup power source for healthcare facilities.
Benefits of Diesel Generators for Temporary Power Needs
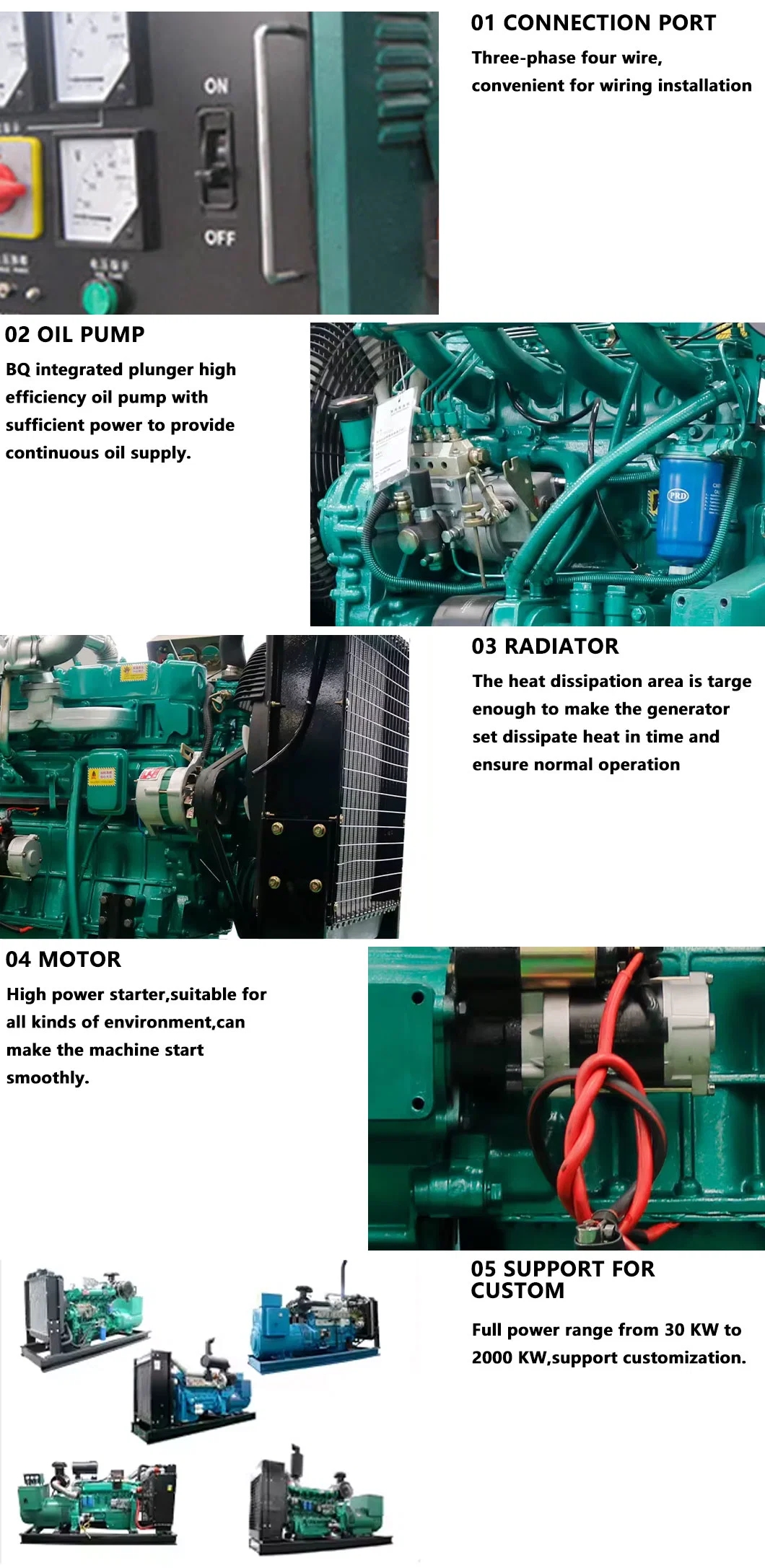
The popularity of diesel generators for temporary power needs can be attributed to several key benefits they offer:
1. Reliability: Diesel generators are known for their reliability and durability, making them a trusted choice for backup power solutions. They can start and provide power quickly, ensuring minimal downtime during outages.
2. Fuel Efficiency: Diesel engines are more fuel-efficient compared to gasoline engines, providing a cost-effective solution for generating power over extended periods. This efficiency translates into longer run times and lower fuel consumption.
3. Longevity: Diesel generators are built to withstand heavy usage and operate for extended periods without significant maintenance requirements. With proper care and periodic servicing, diesel generators can have a long service life.
4. Power Output: Diesel generators are capable of producing high power output, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential backup power to industrial operations. They can handle heavy loads and power multiple devices simultaneously.
5. Easy Maintenance: Diesel generators are relatively low-maintenance compared to other types of generators. Routine tasks such as fuel refilling, oil changes, and filter replacements are simple and can be performed without specialized skills.
6. Versatility: Diesel generators come in a variety of sizes and configurations to meet diverse power needs. From portable units for small-scale use to large industrial generators for powering entire facilities, there is a diesel generator suitable for almost any application.
7. Quick Start-up: Diesel generators can start up quickly and reach full power output within minutes, ensuring that critical systems are powered without delay during emergencies or outages.
Environmental Impact of Diesel Generators
While diesel generators offer numerous advantages for temporary power needs, they also have environmental implications that need to be considered. The combustion of diesel fuel in engines produces emissions that contribute to air pollution and climate change. Key environmental concerns associated with diesel generators include:
1. Air Pollution: Diesel engines emit pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and sulfur dioxide (SO2) that can have adverse effects on air quality and human health. These emissions contribute to smog formation and respiratory illnesses.
2. Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Diesel generators release carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. The combustion of fossil fuels in diesel engines is a significant source of CO2 emissions.
3. Noise Pollution: Diesel generators can produce noise pollution, especially in residential areas or quiet environments. The sound of the engine running can be disruptive and impact the quality of life for those living or working nearby.
Addressing Environmental Concerns
To mitigate the environmental impact of diesel generators and promote sustainability, several measures can be implemented:
1. Use of Cleaner Fuels: Switching to cleaner fuels such as biodiesel or synthetic diesel blends can reduce emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases. These alternative fuels produce fewer harmful emissions and can help lower the environmental footprint of diesel generators.
2. Emission Control Technologies: Installing emission control devices such as particulate filters, selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems, and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems can help reduce the emissions of NOx, PM, and other pollutants from diesel generators.
3. Regular Maintenance: Proper maintenance of diesel generators is essential to ensure optimal performance and minimize emissions. Regular servicing, tuning, and inspection can help improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and extend the lifespan of the generator.
4. Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient practices, such as load management, power factor correction, and efficient system design, can help reduce the overall energy consumption of diesel generators and lower their environmental impact.
Conclusion
Diesel generators play a crucial role in providing temporary power solutions for a wide range of applications, from emergency backup power to construction sites and events. Their reliability, fuel efficiency, power output, and versatility make them a popular choice for ensuring uninterrupted power supply during outages or in remote locations. While diesel generators offer numerous benefits, it is important to address their environmental impact and work towards implementing sustainable practices to minimize emissions and promote environmental stewardship. By understanding 30kw diesel generator for disaster relief working principles, applications, maintenance requirements, and environmental considerations of diesel generators, users can make informed decisions when selecting a temporary power solution for their needs.
